Strengths & Weaknesses of a Restaurant: How to Find and Improve Them for 2026
In the highly competitive food industry, understanding a restaurant’s strengths and weaknesses is crucial for long-term success. Strengths such as excellent customer service, unique menu offerings, or a strong brand identity can set a restaurant apart from its competitors. On the other hand, weaknesses like inconsistent food quality, poor marketing, or high operational costs can limit growth and profitability.
As 2026 approaches, restaurant owners must adopt data-driven strategies to assess performance and enhance their operations. Regularly analyzing customer feedback, financial reports, and market trends helps identify areas that need improvement. By addressing weaknesses and building on strengths, restaurants can enhance efficiency, increase customer satisfaction, and remain resilient in an ever-evolving dining landscape.
What Is a Restaurant Strengths and Weaknesses Analysis?
A strengths and weaknesses analysis is an internal evaluation framework that helps U.S. restaurant owners understand their operations, identify areas for improvement, and create strategies for long-term growth. It’s more than a checklist. It’s a roadmap for building a smarter, more competitive business.
Key Points for a U.S. Restaurant Strengths and Weaknesses Analysis
1. Business Identity Check: Assess whether your brand and story resonate locally.
Example: “Farm & Fork Nashville” highlights partnerships with local Tennessee farms, creating strong community loyalty and reinforcing its farm-to-table identity.
2. Operational Efficiency: Track order accuracy, kitchen prep time, and table turnover.
Example: A Denver bistro implemented an AI-based kitchen display system, reducing food prep errors and cutting wait times by 22%.
3. Menu Relevance: Ensure menu items align with U.S. food trends, dietary demands, and regional tastes.
Example: “Green Plate Austin” regularly updates its vegan and gluten-free options based on local demand, increasing repeat visits from health-conscious diners.
4. Financial Stability: Monitor profit margins and cost of goods sold (COGS).
Example: Many restaurants in New York City now use predictive analytics software like MarketMan to forecast inventory needs and control food waste, improving margins.
5. Technology Integration: POS, AI chatbots, and online booking platforms are now standard.
Example: Urban Bowl LA uses AI forecasting to predict popular dishes daily, reducing food waste by 15% and improving kitchen efficiency.
6. Customer Engagement: Build community through social media storytelling, loyalty programs, and events.
Example: “The Local Table Chicago” hosts Instagram live cooking demos and personalized loyalty discounts, boosting engagement and repeat customers.
7. Workforce Management: Creating clear career paths and training programs reduces turnover.
Example: “Coastline Seafood Grill” in San Diego introduced cross-training programs and employee mentorship, lowering annual staff turnover by 18%.
This analysis helps restaurants in the U.S. strengthen internal systems, adapt to market trends, and deliver consistently superior dining experiences.
What Are Some Common Strengths That Drive Restaurant Success?
The strengths of restaurant business often define its ability to survive competitive shifts. Successful restaurants combine operational excellence, innovation, and adaptability to stand out in a crowded market.
Key Strengths That Drive Success
-
High-Quality Ingredients: “Blue Coast Grill” in Seattle built its brand around traceable, sustainable seafood sources.
-
Experienced Culinary Team: Skilled chefs who introduce seasonal specials based on customer data.
-
Efficient Service Flow: AI-enabled table management systems that reduce peak-hour bottlenecks.
-
Strong Vendor Relationships: Partnering with hyperlocal farms for consistency and lower delivery costs.
-
Effective Leadership: Transparent management that motivates and retains employees.
-
Customer Retention Programs: Personalized rewards via digital wallets, “CraveClub” app users spend 12% more per visit.
-
Clean & Inviting Environment: Post-pandemic diners still rate visible hygiene as a top trust factor.
-
Financial Discipline: Smart portion control and supplier negotiations keep costs stable despite inflation.
These foundational strengths directly influence food quality, service excellence, and brand reputation, the true pillars of restaurant success in the U.S.
What Are Some Common Weaknesses That Can Hold A Restaurant Back?
Understanding the weakness of restaurant business is just as important as identifying what it does well. Even thriving restaurants face hidden operational or marketing gaps that can reduce profitability.
Operational Weaknesses
-
Overdependence on Signature Dishes: A Chicago pizzeria lost customers when its best-seller faced ingredient shortages, a reminder to diversify menu highlights.
-
Ineffective Staff Communication: Order errors spike during shift changes; staff messaging apps like 7shifts can help.
-
Outdated Equipment: Slows service and increases energy costs, a hidden profit drain.
Marketing & Brand Weaknesses
-
Inconsistent Social Presence: A Dallas café saw engagement drop 40% after pausing its Instagram posts, proving consistency builds trust.
-
Unclear Brand Positioning: A bistro marketing itself as both family-friendly and upscale confused customers.
-
Ignoring Reviews: Failing to respond to negative Yelp or Google reviews erodes credibility.
Menu & Experience Weaknesses
A weakness of restaurant example is offering too many similar dishes without a signature item that differentiates your brand.
-
Slow Trend Adaptation: No gluten-free or low-carb options, Health-conscious customers move on.
-
Overcomplicated Menu: A 60-item menu at a Florida seafood restaurant led to slower prep and higher waste.
-
Weak Takeout Strategy: Restaurants relying solely on dine-in miss online revenue opportunities, especially during local events or bad weather.
By addressing these weaknesses with practical solutions, restaurant owners can improve operational efficiency, increase customer satisfaction, and boost long-term profitability.
Why To Find The Strengths And Weaknesses Of a Restaurant?
Analyzing your strengths and weaknesses reveals insights that drive smart decisions. It helps uncover what’s working, what’s not, and where new opportunities lie.
Reasons to Analyze Strengths and Weaknesses
-
Uncover Hidden Customer Preferences: Discover which dishes drive repeat visits via POS data.
-
Detect Operational Blind Spots: Identify inefficiencies like prep bottlenecks.
-
Reveal Innovation Opportunities: Test new offerings, like a “Chef’s Table Tuesday” night for loyal customers.
-
Assess Technology Effectiveness: Ensure digital tools are integrated, not just installed.
-
Anticipate Market Shifts: Predict demand for delivery-only kitchens or sustainable packaging.
-
Optimize Resource Allocation: Invest in what drives loyalty, such as a refreshed loyalty app.
-
Boost Community Engagement: Collaborate with local causes or food festivals to build authentic connections.
Explore this article on cybersecurity on the menu: how restaurants can stay ahead of threats, offering insights on protecting sensitive customer data and safeguarding your restaurant’s digital infrastructure from cyberattacks.
How To Identify Your Restaurant’s Strengths And Weaknesses?
Sustainable growth requires analyzing operations, customers, and market trends beyond sales and reviews. A structured approach turns strengths into opportunities and minimizes weaknesses.
Key Points to Identify Strengths and Weaknesses (with Impact Percentages):
-
Customer Experience Mapping (30% Impact): Track all touchpoints, reservations, arrival, dining, and payment.
-
Operational Process Audits (25% Impact): Examine back-of-house workflow, inventory handling, and prep times.
-
Advanced Data Insights (20% Impact): Analyze POS, loyalty programs, and order patterns.
-
Staff Engagement & Skills Assessment (15% Impact): Evaluate cross-training, initiative, and communication.
-
Market Trend & Competitor Analysis (10% Impact): Monitor industry shifts and local competition.
SWOT Analysis of Restaurant
Here’s a practical SWOT analysis of restaurant to demonstrate how internal and external factors influence success:
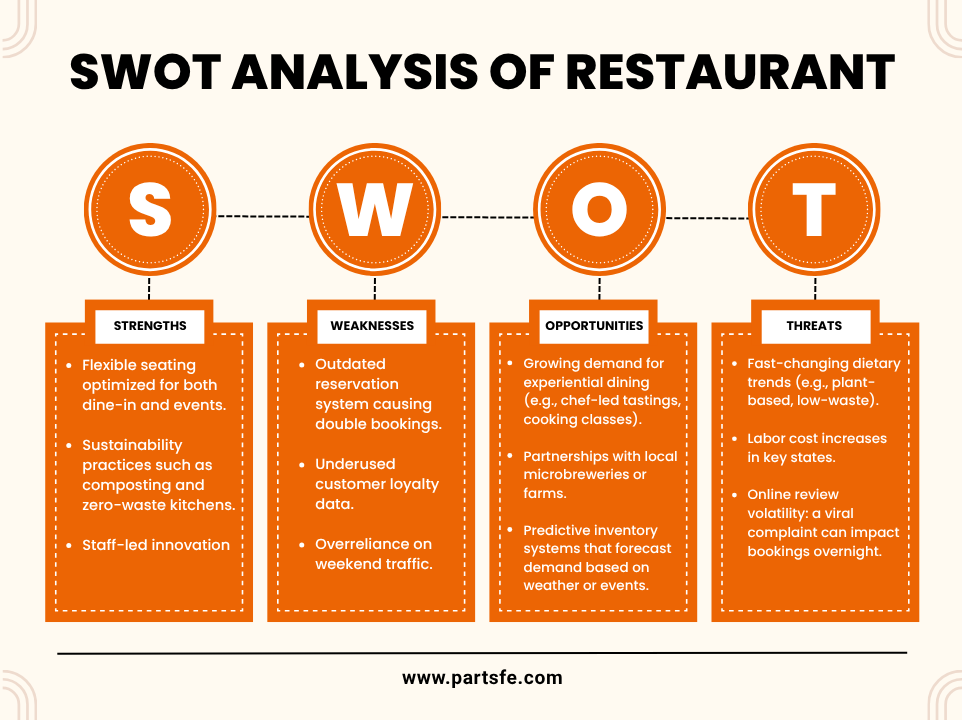
Check out this article on food service industry evolution in 2025: unveiled by consumer adoption tracking, exploring how shifting consumer preferences are driving innovation and transformation in the foodservice sector.
What Are The Strategies To Improve Weaknesses And Amplify Strengths?
To gain a real competitive edge, restaurants must adopt strategies that uncover hidden potential and resolve overlooked gaps. Here are fresh, actionable approaches:
Step 1: Identify Strengths
-
Strength Bundling : Combine multiple strengths into one initiative (e.g., fast service + menu innovation)
-
Strength Quantification : Track measurable KPIs for top-performing areas
-
Cross-Department Strength Sharing : Apply high-performing practices from one team to others
-
Community Leverage : Use a strong local reputation to organize events or workshops
Step 2: Identify Weaknesses
-
Operational Stress Testing : Simulate real-world challenges to reveal gaps
-
Controlled Experimentation : Test small-scale process improvements before full implementation
-
Hidden Resource Optimization : Redeploy underused assets (staff skills, tools, menu items)
-
Weakness Prioritization Matrix : Categorize weaknesses by impact and urgency
-
Peer Benchmarking : Compare processes with other restaurants to uncover blind spots
Step 3: Implement & Monitor
-
Track progress of amplified strengths with KPIs
-
Measure improvements in weak areas with specific metrics
-
Adjust strategies based on results and customer feedback
Step 4: Continuous Improvement Loop
-
Repeat assessment and refinement periodically
-
Integrate lessons learned into daily operations
-
Ensure strengths remain strong and weaknesses are systematically reduced
Building a Long-Term Growth Plan for 2026 and Beyond
Planning for the future means looking beyond immediate operations and focusing on strategic resilience and innovation. Restaurants that proactively assess market shifts, anticipate customer expectations, and adopt scalable systems are better positioned to grow sustainably. Emphasizing continuous learning, flexible menu strategies, and operational adaptability ensures long-term relevance in a competitive industry.
Key Takeaways:
-
Prioritize adaptive supply chain strategies to handle unexpected market fluctuations.
-
Invest in staff skill diversification to enhance operational flexibility and creativity.
-
Explore a modular menu design that allows rapid introduction of trending or seasonal items.
-
Leverage technology to monitor hidden inefficiencies and streamline internal processes.
-
Develop a culture of innovation where small experimental initiatives guide larger growth decisions.
Creating a growth plan is about future-proofing the restaurant. Focusing on adaptability, experimentation, and operational flexibility ensures long-term profitability and a stronger market position in 2026 and beyond.
Looking to keep your restaurant equipment running smoothly in 2026? PartsFe has you covered with replacement parts from leading brands like Vulcan, Hobart, and Frymaster. Whether you need burners, thermostats, or door gaskets, PartsFe offers high-quality solutions to keep your commercial kitchen performing efficiently and reliably all year round.
References:
https://www.wekivaculinary.org/
https://restaurant.org/
FAQs
What is a SWOT analysis for the restaurant industry?
A SWOT analysis for a restaurant evaluates Strengths (e.g., unique menu), Weaknesses (e.g., poor location), Opportunities (e.g., emerging trends like delivery services), and Threats (e.g., competition or rising food costs). It helps restaurants identify areas for improvement and growth strategies.
What is the 30-30-30 rule for restaurants?
The 30-30-30 rule in restaurants refers to allocating 30% of your budget for food, 30% for labor, and 30% for overhead costs, leaving 10% for profit. Following this guideline helps maintain balance in operational costs and maximize profitability
What is the most common mistake that restaurants make?
One of the most common mistakes restaurants make is underpricing their menu items, leading to insufficient margins. Poor marketing and failure to adapt to consumer trends also contribute to a restaurant’s downfall.
How much does it cost to set up a small restaurant in the U.S.?
It typically costs between $150,000 and $500,000 to start a small restaurant. The exact amount depends on location, size, and the type of equipment and permits required.
How do I calculate the break-even point for a restaurant?
Add all fixed and variable costs, then divide by the average price per customer. This helps determine how many sales are needed to cover expenses.











